
A new supply chain report says that OLED iPads, reported to be launching in 2024, will offer more than just improved display quality.
Apple is said to be employing an advanced OLED manufacturing process for the first time, which allows the display to be both thinner and lighter …
Background
If you need a reminder of the four-generation display journey Apple is on – with OLED as step three – you can find that here.
Apple analyst Ming-Chi Kuo last year suggested that the first OLED iPad would launch in 2022, but subsequently said this plan had been abandoned.
Apple has three display suppliers, and all three have been reported to be working on a new generation of OLED panel technology likely geared toward Apple.
Samsung’s panel design was said to double the brightness and boost longevity. LG was reported to be readying itself for orders for OLED iPad displays, preparing to double the production of a plant dedicated to making advanced displays in the right size range for iPads. Finally, BOE was recently said to be joining the OLED iPad panel party – though the company isn’t exactly in Apple’s good books at present.
Apple prototyping OLED iPads
We learned recently that Samsung was working on a new advanced OLED production line specifically for Apple, and ET News now has more details.
Apple will also introduce the iPad OLED display dry etching process for the first time. Display dry etching is a process of removing unnecessary parts using chemical technology when making thin film transistor (TFT) circuit patterns. The display can be etched to make the display thinner and lighter […]
Along with this, Apple is developing special coatings to increase durability of the thin panel from the etching process. Samsung and LG Display are expected to supply the OLED panels.
Apple is said to be at the prototyping stage.
Apple is producing final prototypes of OLED iPads with major domestic display partners. As this is the first time OLED will be used in a tablet PC, Apple is creating several prototypes and repeating the testing process several times.
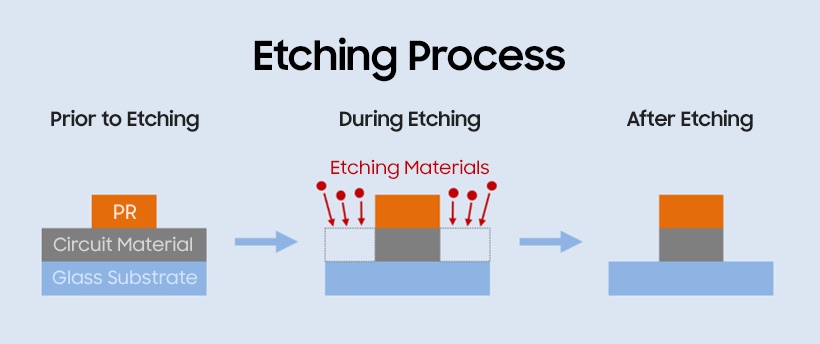
Why is this a more advanced process?
Etching is the process of removing unwanted material from a display module, to reduce weight. Conventional OLED production uses a wet etching process, while the more advanced approach is dry etching. Here’s how Samsung Display explains the difference when pitching the dry etching process to clients like Apple:
Wet etching uses a solution to induce a chemical reaction to carve out a pattern, whereas dry etching removes specific parts by using reactive gas and ions.
Wet etching, compared to its dry counterpart, is cheaper, faster, and simpler. However, it is less precise compared to the dry method and it carries the risk of contamination due to the use of chemical substances in the process. Dry etching is more suitable to create a microcircuit thanks to its ability to easily target specific parts for etching. However, it is expensive, complex, and slow to process.
Dry etching is often referred to as plasma etching. In this process, an etching gas is injected into the vacuum chamber where the substrate is placed, and then electrical energy is provided into the chamber to create plasma. Afterward, ions that gain high levels of kinetic energy from the ionized gas are accelerated by the electrodes on the substrate so that the atomic bond in the circuit material is broken, which enables etching. Dry etching is the preferred method used for the majority of microcircuit patterns required for high-resolution displays today.
Photo: Henry Ascroft/Unsplash
FTC: We use income earning auto affiliate links. More.






Comments