GigaOM today published a lengthy piece on the state of the solar and fuel cell farm installations that Apple has been building in North Carolina in recent years.
After a visit to the 100-acre, 20 megawatt (MW) solar farm, 10MW fuel cell farm, and another 20 MW solar panel farm situated close to Apple’s North Carolina iCloud data center, the report gives a pretty in-depth look into Apple’s operations, from how its fuel cells work right down to the sheep that eat the grass on its solar farm:
The solar farm across from the data center has over 50,000 panels on 100 acres, and it took about a year to build the entire thing….Each solar panel on Apple’s farms has a microcontroller on its back, and the panels are attached to long, large trackers (the steel poles in the picture). During the day, the computers automatically and gradually tilt the solar panels so that the face of the panels follow the sun throughout the day. The above picture was taken in the late morning, so by the end of the day, the panels will have completely rotated to face where I was standing. The trackers used are single-axis trackers, which basically means they are less complex and less expensive than more precise dual-axis trackers.
You can see in the above picture that the grass is neatly maintained. Apple manages the grass under the panels in a variety of ways, but one of those is a little more unusual. Apple works with a company that ropes in sheep that eat the grass on a portion of the solar farm; when the sheep finish grazing on one spot, they’re moved to the next.
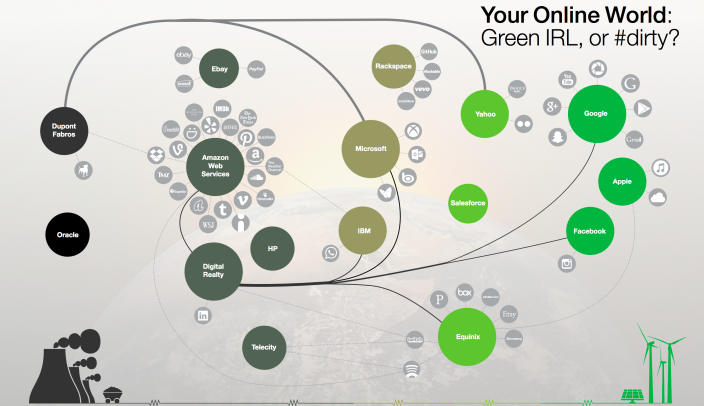
 The site decided to take a look into Apple’s decision to take renewable energy into its own hands just as North Carolina utility Duke Energy is requesting that the state allow it to sell clean energy to large corporate customers. Google is one of the large companies interested in purchasing clean energy from the utility, but the hundreds of millions Apple has invested into its own renewable energy efforts have so far made it self-sufficient. The report notes Apple’s two solar farms, along with its fuel cell farm, are producing more than it needs to power its data center by around 10MW:
The site decided to take a look into Apple’s decision to take renewable energy into its own hands just as North Carolina utility Duke Energy is requesting that the state allow it to sell clean energy to large corporate customers. Google is one of the large companies interested in purchasing clean energy from the utility, but the hundreds of millions Apple has invested into its own renewable energy efforts have so far made it self-sufficient. The report notes Apple’s two solar farms, along with its fuel cell farm, are producing more than it needs to power its data center by around 10MW:
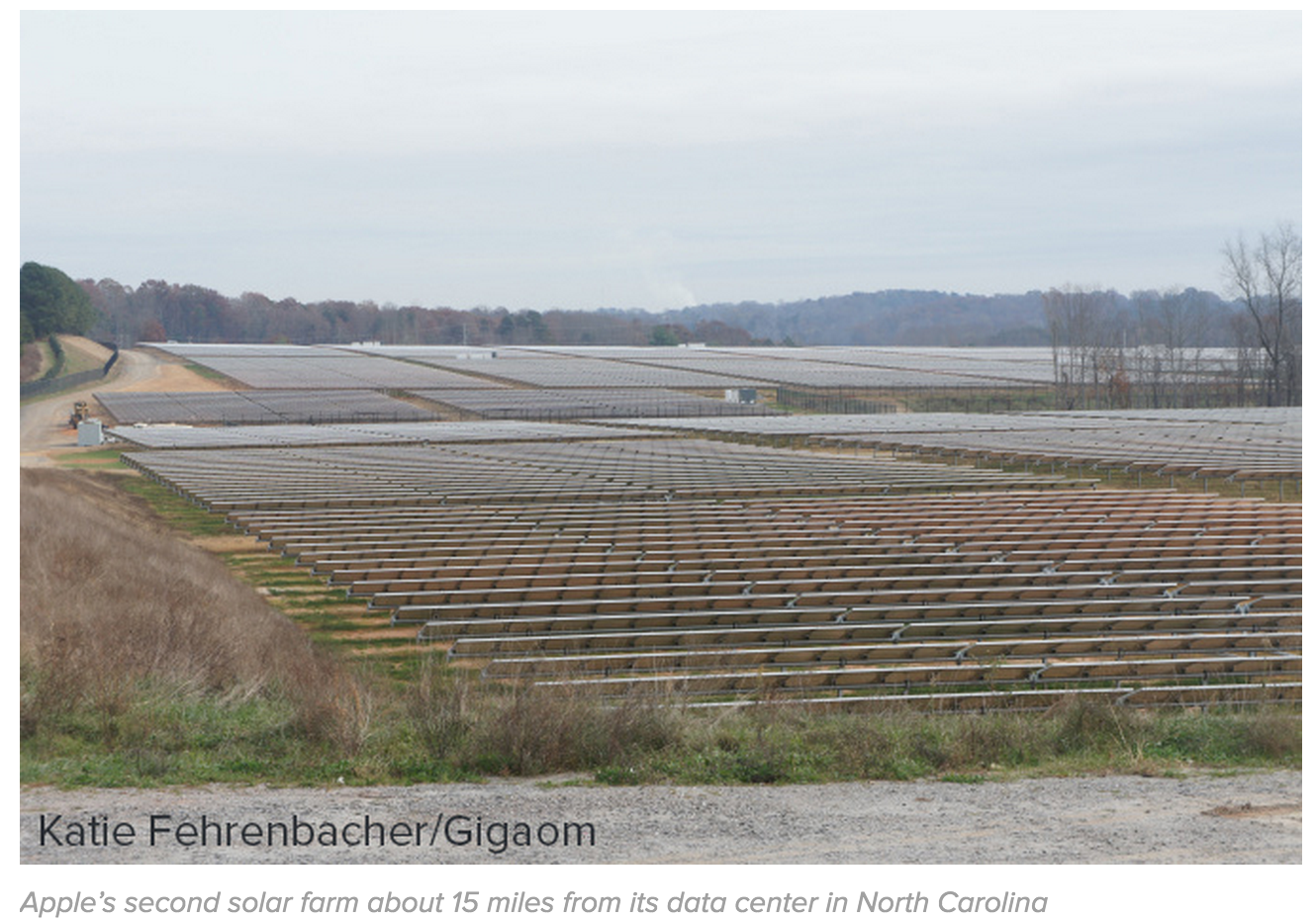
Apple’s second 20 MW solar panel farm, which is about 15 miles away from the data center near the town of Conover, North Carolina, is also up and running. All told, the three facilities are creating 50 MW of power, which is about 10 MW more than what Apple’s data center uses. Because of state laws, the energy is being pumped into the power grid, and Apple then uses the energy it needs from the grid. But this setup also means Apple doesn’t need large batteries, or other forms of energy storage, to keep the power going when the sun goes down and its solar panels stop producing electricity.
The full feature on GigaOM is worth checking out if you’re interested in Apple’s renewable energy projects.



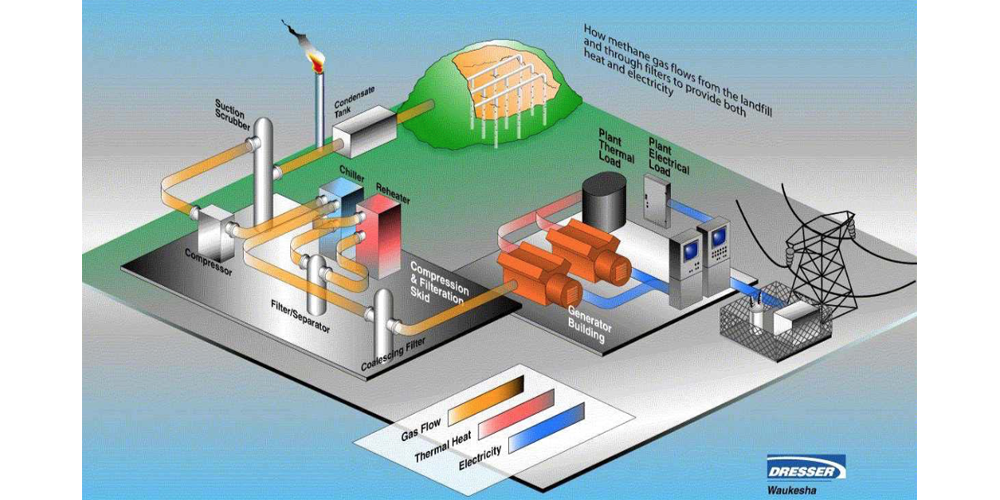




 The site decided to take a look into Apple’s decision to take renewable energy into its own hands just as North Carolina utility Duke Energy is requesting that the state allow it to sell clean energy to large corporate customers. Google is one of the large companies interested in purchasing clean energy from the utility, but the hundreds of millions Apple has invested into its own renewable energy efforts have so far made it self-sufficient. The report notes Apple’s two solar farms, along with its fuel cell farm, are producing more than it needs to power its data center by around 10MW:
The site decided to take a look into Apple’s decision to take renewable energy into its own hands just as North Carolina utility Duke Energy is requesting that the state allow it to sell clean energy to large corporate customers. Google is one of the large companies interested in purchasing clean energy from the utility, but the hundreds of millions Apple has invested into its own renewable energy efforts have so far made it self-sufficient. The report notes Apple’s two solar farms, along with its fuel cell farm, are producing more than it needs to power its data center by around 10MW: